Functional group polarity-modulated formation of liquid crystals of amphiphilic cyclodextrins
Today’s cyclodextrin:
At CarboHyde, we also deal with amphiphilic CDs; this application from this Canadian collaboration caught my attention.
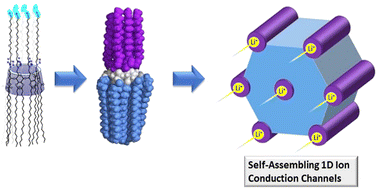
Pseudo-face-to-face symmetry in the native CDs represents a distinctive advantage to designing amphiphilic materials capable of self-assembly into liquid crystals. In this work, a new family of amphiphilic β-CD derivatives possessing 14 stearoyl chains (non-polar) and 7 functionalized tetraethylene glycols were synthesized using an improved design and more efficient chemistry, and the synthetic targets showed excellent ability to form stable hexagonal columnar mesophases. Studies of a lithium composite revealed fast local Li-ion exchange processes with very low activation energies, suggesting the benefit of using these materials as potential electrolytes for high ionic conductions. The results from this work can guide the design of future generations of CD-based LC materials for ion conduction.
University of Calgary – Austin Che, Simon Trudel-Lachance, Jayar Espejo, Chang-Chun Ling
University of Alberta – Diganta Sarkar, Vladimir Michaelis
Simon Fraser University – Carson Zellman, Vance Williams
See the full article here: Functional group polarity-modulated formation of liquid crystals of amphiphilic cyclodextrins