Reduction of thyroid radioactive iodine exposure by oral administration of cyclic oligosaccharides
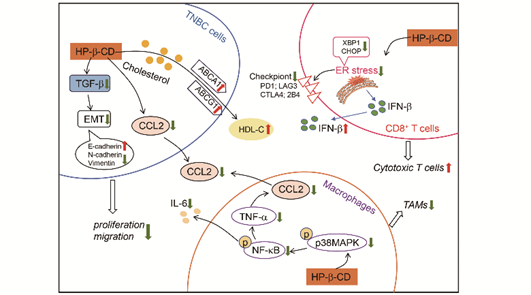
Radioactive iodine may cause thyroid cancer and hypofunction and accordingly must be properly managed. If the absorption of radioactive iodine is suppressed, it can be expected to lead to a reduction in thyroid exposure. This study the inhibition of radioactive iodine absorption by the oral administration of α-cyclodextrin is shown in a murine model. The uptake of radioactive iodine into the thyroid gland in mice administered with radioactive iodine and an α-cyclodextrin solution was approximately 40% lower after 24 h. The finding that oral uptake of α-cyclodextrin has an inhibitory effect on the transfer of radioactive iodine to the thyroid gland has potential for application in many fields such as food, pharmaceuticals, nuclear emergency preparedness, and medicine.
Kumamoto University, JAPAN
See the full article on nature.com