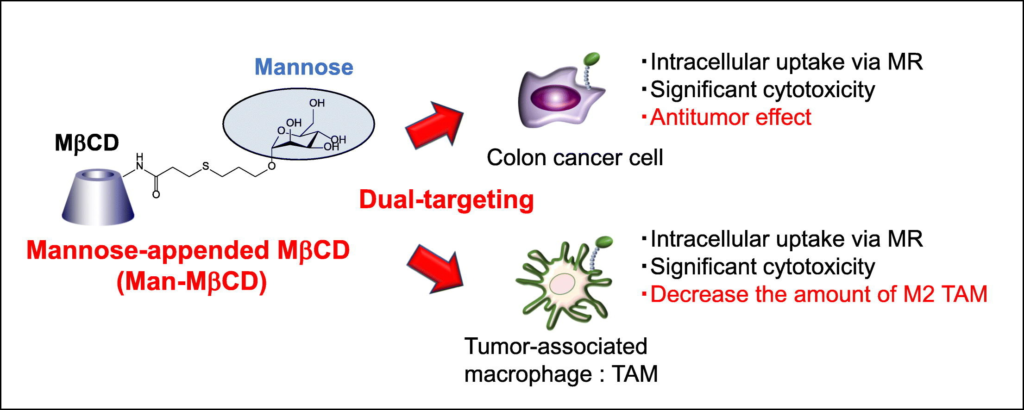
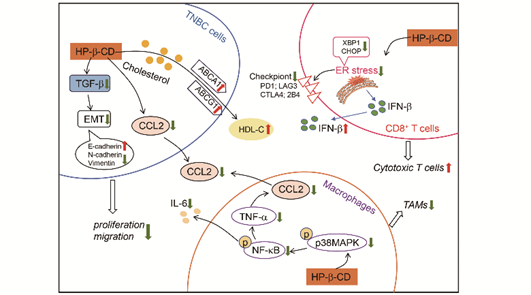
Lipid-based RNA formulations suitable for therapy
today’s cyclodextrin:
In this invention, BioNTech SE provides a method of producing a composition comprising RNA lipoplex particles. The main focus of the description is antitumoral therapy.
In the formulation itself, the aqueous colloidal suspension of liposomes is combined with an aqueous solution comprising RNA, thereby producing the composition comprising RNA lipoplex particles. The formulation requires frozen storage conditions; hence the use of cyroprotectant is necessary. The invention proposes mono- di- and oligosaccharides to protect such compositions, including various cyclodextrins and cyclodextrin polymers.
The use of cyclodextrins as cryoprotectants and stabilizers in biopharmaceutical formulations is an emerging technology.
Dr. Hossam Hefesha, Heinrich Haas, Ferdia Bates, Christian Hotz
Katalin Karikó
See the full patent Patentscope