Cyclodextrin nanoparticles in targeted cancer theranostics
Today’s cyclodextrin:
Cyclodextrin nanoparticles in targeted cancer theranostics
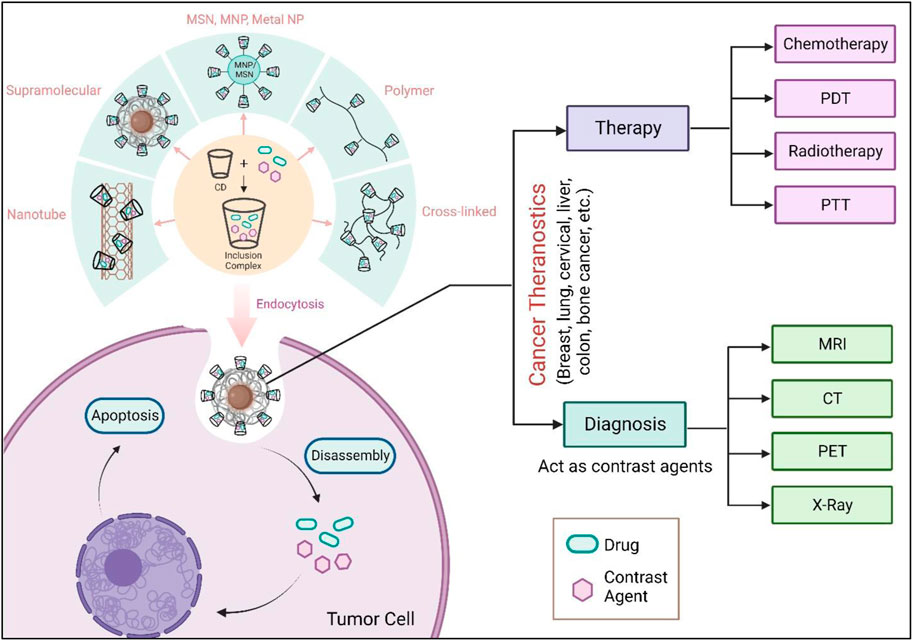
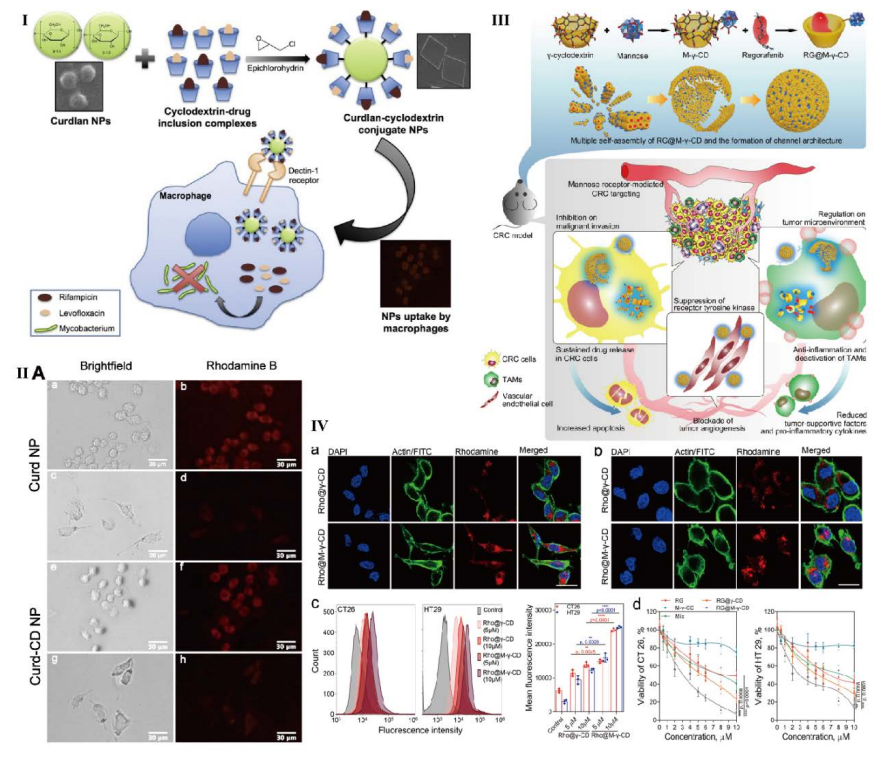
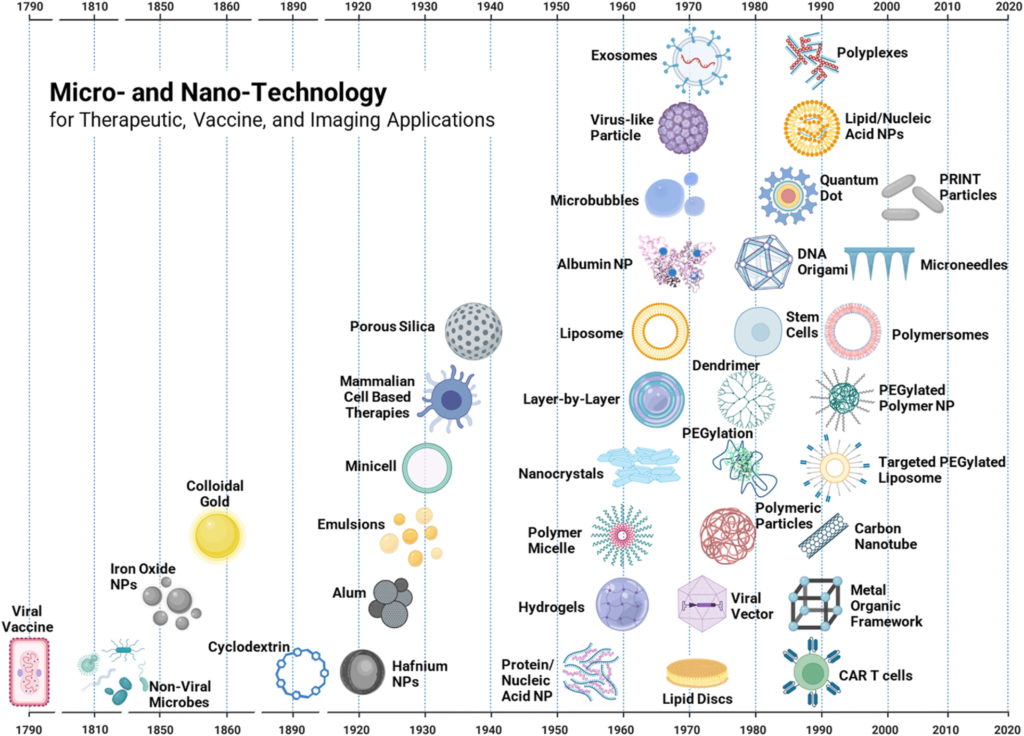
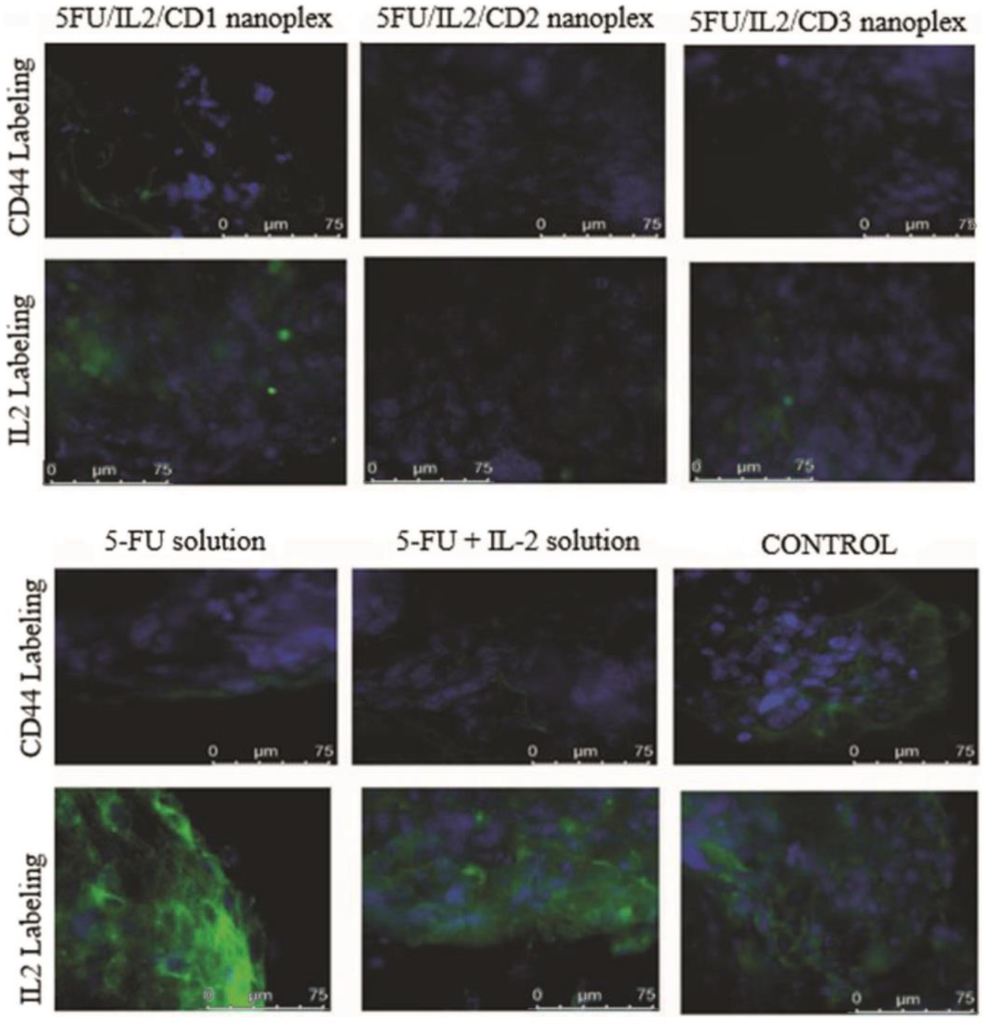
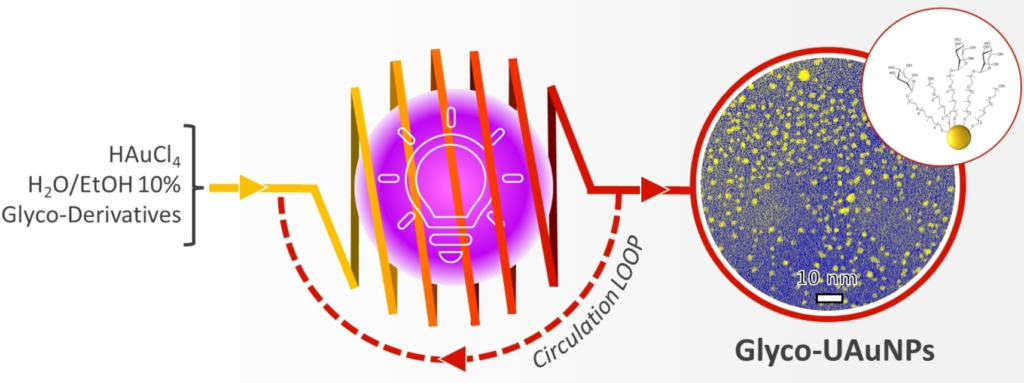
The field of cancer nanotheranostics is rapidly evolving, with cyclodextrin (CD)-based nanoparticles emerging as a promising tool. CDs, serving as nanocarriers, have higher adaptability and demonstrate immense potential in delivering powerful anti-cancer drugs, leading to promising and specific therapeutic outcomes for combating various types of cancer. The unique characteristics of CDs, combined with innovative nanocomplex creation techniques such as encapsulation, enable the development of potential theranostic treatments. The review here focuses mainly on the different techniques administered for effective nanotheranostics applications of CD-associated complex compounds in the domain of cancer treatments. The experimentations on various loaded drugs and their complex conjugates with CDs prove effective in in vivo results. Various cancers can have potential nanotheranostics cures using CDs as nanoparticles along with a highly efficient process of nanocomplex development and a drug delivery system. In conclusion, nanotheranostics holds immense potential for targeted drug delivery and improved therapeutic outcomes, offering a promising avenue for revolutionizing cancer treatments through continuous research and innovative approaches.
Frontiers | Cyclodextrin nanoparticles in targeted cancer theranostics (frontiersin.org)