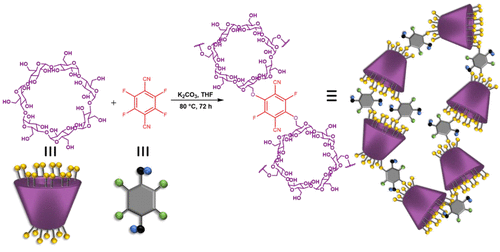
Sustained Delivery of Cu(II)-Based DNA Intercalators by Nanometer-Sized Cyclodextrin-Based Porous Polymers
Apparently, cyclodextrin-based oligonucleotide delivery is becoming a hot research topic. This recent study from University of Nova Gorica – Tina Škorjanc, PhD, Damjan Makuc, Nora Kulak, and Valant Matjaz presents a cyclodextrin porous polymer to form nanometer-sized particles and used as a delivery vehicle for metal-free and Cu(II)-metalated anthraquinone-based DNA intercalators.