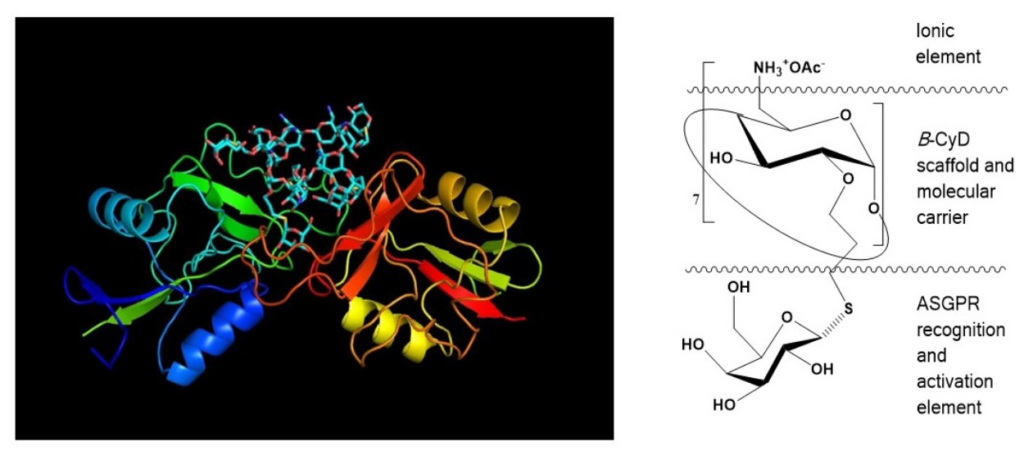
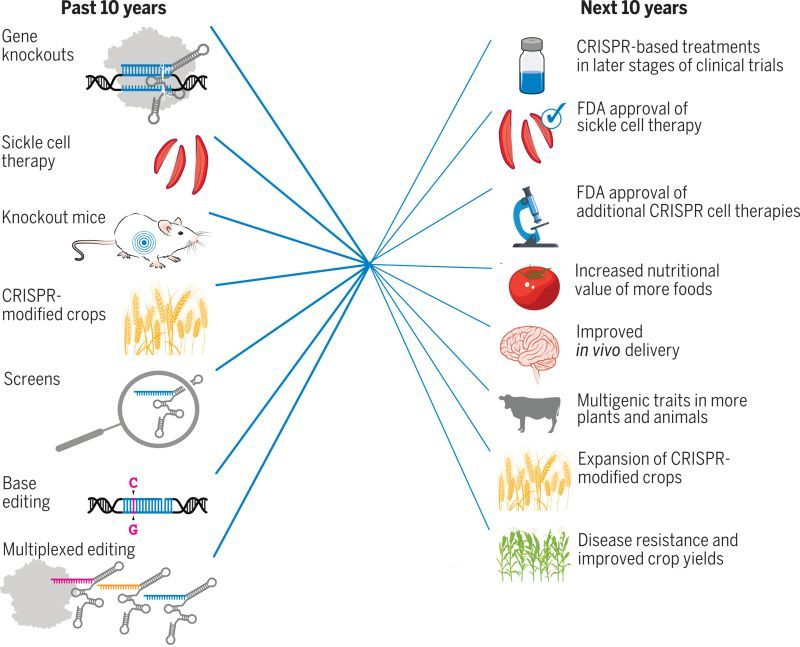
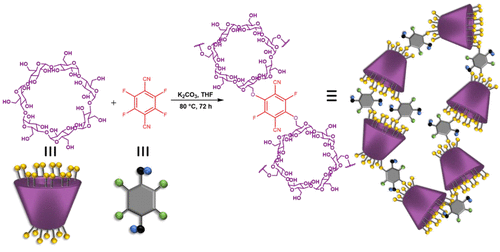
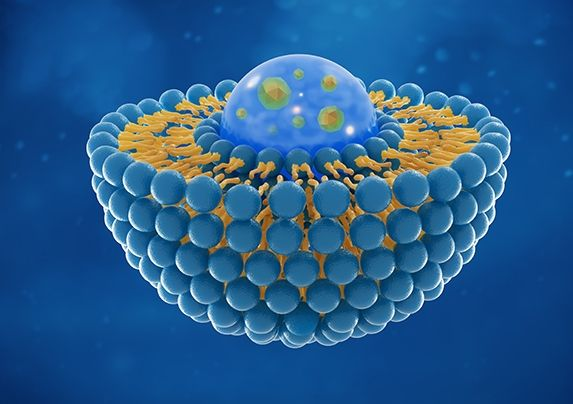
How do you see the future of cell and gene therapy?
Our concise outlook is the following:
Transformational Potential: Cell and gene therapies are revolutionizing how we treat diseases, promising to cure certain conditions.
They remain at the forefront of healthcare innovation.
Fast-Growing Field: These therapies are the fastest-growing therapeutics areas, with over 50 new in vivo and ex vivo gene therapy launches planned in the next few years.
Challenges and Innovation: While promising, cell and gene therapies require substantial innovation to unlock their full potential for patients. Scaling digital and analytics in discovery and R&D is part of the solution.
Market Resilience: Despite the disruptions caused by the pandemic, stakeholders, including CGT innovators, healthcare providers, and CDMOs, are optimistic that positive developments lie ahead.
Viral-Vector Therapies: Viral-vector gene therapies are here to stay, but addressing challenges and strategizing for patient access is critical for their success.
Overall, the outlook is positive, but ongoing research, regulatory advancements, and manufacturing innovations will shape the future of cell and gene therapy. 🌟