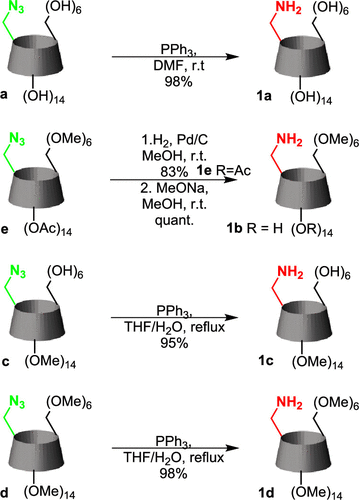
Mirror-image cyclodextrins
today’s cyclodextrin:
Do you often take a good look in the mirror?
Nobel laureate Sir Fraser Stoddard, Daniel W. Armstrong, and their team report the syntheses of three mirror-image CDs—namely, α-, β- and γ-L-CDs, which are composed of six, seven and eight α-1,4-linked L-glucopyranosyl residues, respectively.
The availability of L-CDs has enabled the elucidation of an unprecedented chiral self-sorting of a racemic modification of β-CDs in the solid state and an investigation of the chiral recognition of enantiomeric fenchone by α-L-CD. This research identifies a missing piece of the cyclodextrin jigsaw and sets the stage for scientists to explore the mirror-image world of naturally occurring CDs.
Mirror-image cyclodextrins | Nature Synthesis