Where do you expect its greatest impact in the future?
For more than a decade, the CRISPR toolbox and its applications have profoundly changed biological research, enabling advances through applications in plants, animals, and humans.
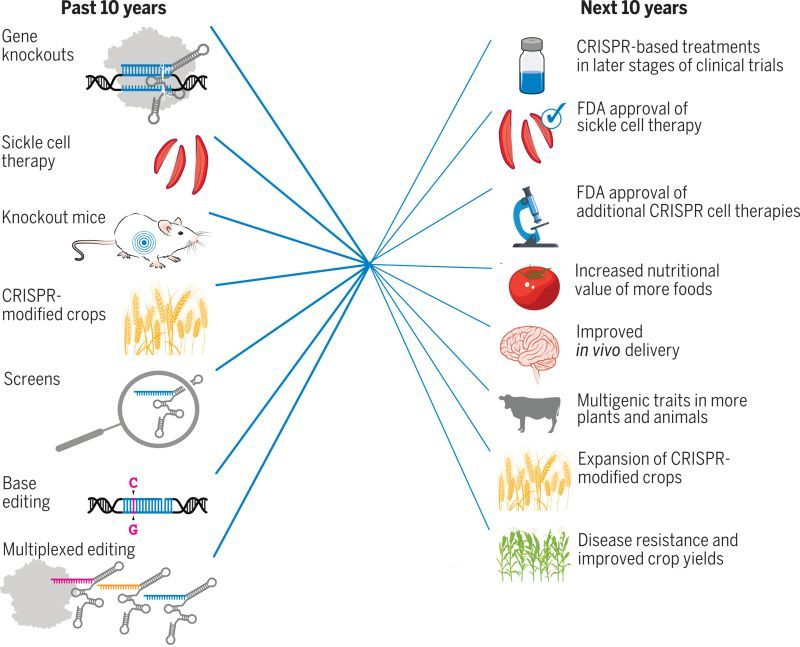
For more than a decade, the CRISPR toolbox and its applications have profoundly changed biological research, enabling advances through applications in plants, animals, and humans.

⚫ Alzheimer’s disease takes a toll on not just the people suffering from the disease but also on their loved ones and caregivers in a way that almost no other illness does.
⚫ The Alzheimer’s disease market is projected to experience robust growth at a compound annual growth rate of 20% from $2.2 billion in 2020 to $13.7 billion in 2030!
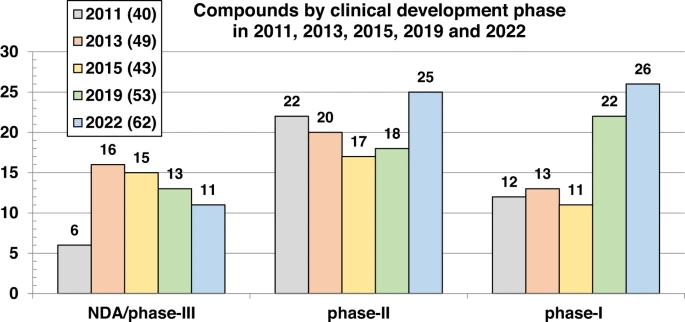
🔶 Drug Development Pipeline:
🔸 187 current trials assessing 141 unique drugs
🔸 Phase 3: 36 drugs
🔸 Phase 2: 87 drugs
🔸 Phase 1: 31 drugs
🔷 Phase 3 has 36 agents in 55 trials:
🔹 DMT*-Biologics: 9 (25%)
🔹 DMT*-Small molecules: 15 (42%)
🔹 Putative cognitive-enhancers: 5 (14%)
🔹 Neuropsychiatric symptoms: 7 (19%)
*DMT stands for disease-modifying therapies
🔶 Most Common Targets:
🔸 Transmitter receptors, amyloid, synaptic function, and inflammation
🔷 58 new drugs have entered the pipeline in the past year!
🔷 28% of candidate therapies are repurposed from other diseases!
⚫Despite the hype, controversy, and occasional scandal surrounding the approval of Alzheimer’s drugs, and the disappointing reports of the ineffectiveness of recently approved drugs, many companies are still dedicating time and resources to finding a potential cure for this debilitating disease. This gives hope that the future is bright for those living with Alzheimer’s.
🔶 Learn more:
🔸 Alzheimer’s disease drug development pipeline: 2023 – Cummings – 2023 – Alzheimer’s & Dementia: Translational Research & Clinical Interventions – Wiley Online Library
🔸 Alzheimer’s Drug Market To Hit $13B As FDA Approvals And Insurance Coverage Escalate (forbes.com)
Great collection from Maryam Daneshpour
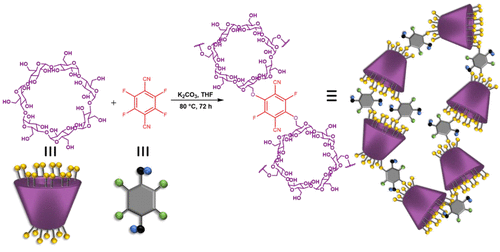
Apparently, cyclodextrin-based oligonucleotide delivery is becoming a hot research topic. This recent study from University of Nova Gorica – Tina Škorjanc, PhD, Damjan Makuc, Nora Kulak, and Valant Matjaz presents a cyclodextrin porous polymer to form nanometer-sized particles and used as a delivery vehicle for metal-free and Cu(II)-metalated anthraquinone-based DNA intercalators.
Hungary is just a small grain on the beach of the pharma industry, yet from time to time we also make remarkable discoveries.
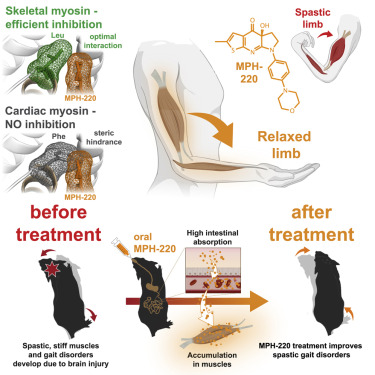
Today, its Motorpharma Ltd. a spin-off from Eötvös Loránd University that makes us proud by starting to dose their lead compounds MPH-220 to humans in Texas.
Mate Gyimesi, András Málnási-Csizmadia et al first published in 2020 in Cell about MPH-220, whish is targeting skeletal muscle myosin and can enabled muscle relaxation, in human and model systems, without cardiovascular side effects and improved spastic gait disorders after brain injury in a disease model. MPH-220 provides a potential nervous-system-independent option to treat spasticity and muscle stiffness.
Muscle spasticity after nervous system injuries and painful low back spasm affect more than 10% of global population. Current medications are of limited efficacy and cause neurological and cardiovascular side effects because they target upstream regulators of muscle contraction. Direct myosin inhibition could provide optimal muscle relaxation; however, targeting skeletal myosin is particularly challenging because of its similarity to the cardiac isoform.
About Motorpharma: https://motorpharma.com/
Fascinating therapeutic application of cyclodextrins have been published by Beren Therapeutics. Earlier the company already patented the use in the therapy of familial hypercholesterolemia, now they propose using hydroxypropyl-BCD against hypertriglyceridemia.
In the 2nd patent composition and purification is reported of a compounds that has a surprisingly high DS (DS-10 being the main component), which composition is far from the materials used as excipients.
WO2023156970 TREATMENT OF HYPERTRIGLYCERIDEMIA WITH 2-HYDROXYPROPYL-BETA-CYCLODEXTRIN (wipo.int)
Do you think we are putting enough effort in developing novel antibiotics?
The need for new antibacterial drugs to treat the increasing global prevalence of drug-resistant bacterial infections has clearly attracted global attention, with a range of existing and upcoming funding, policy, and legislative initiatives designed to revive antibacterial R&D. Despite the promising early-stage antibacterial pipeline, it is essential to maintain funding for antibacterial R&D and to ensure that plans to address late-stage pipeline issues succeed.
See the full article here:
Antibiotics in the clinical pipeline as of December 2022 | The Journal of Antibiotics (nature.com)
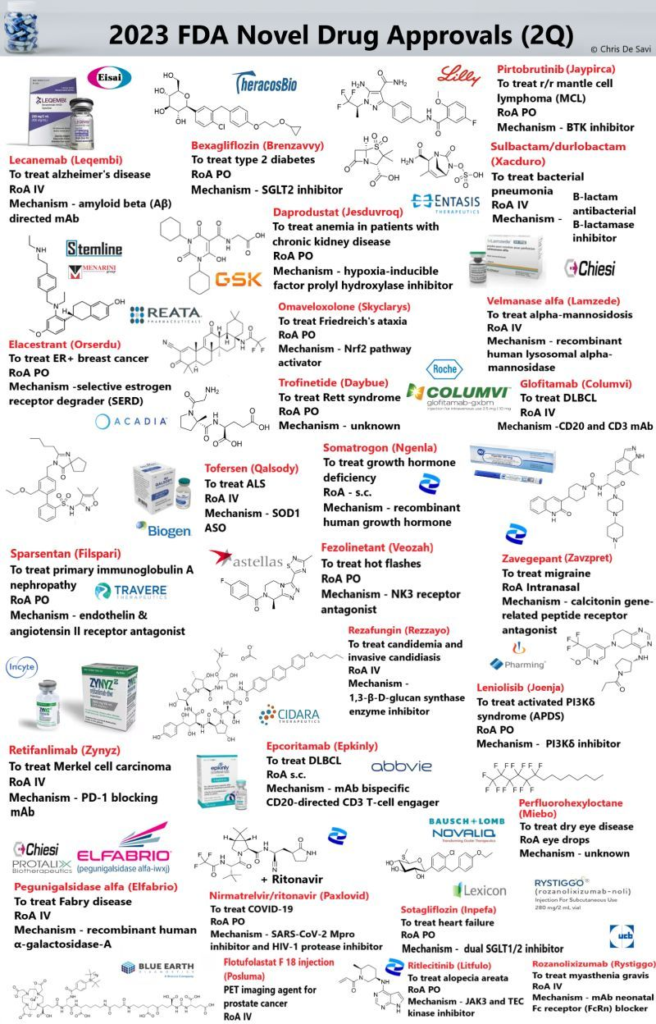
26 new drugs approved by the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) for 1H! Lots of exciting new mechanisms and modalities.
Highlights from the 2Q include –
💉 Tofersen (Qalsody), an antisense oligonucleotide indicated for the treatment of adult amyotrophic lateral sclerosis caused by SOD1 mutation.
💉 Pegunigalsidase alfa (Elfabrio), a recombinant form of human α-galactosidase-A indicated for long-term enzyme replacement therapy in patients with Fabry disease.
💊 Fezolinetant (Veozah), a selective neurokinin-3 (NK3) receptor antagonist used to treat moderate to severe vasomotor symptoms due to menopause.
👁 Perfluorohexyloctane (Miebo) is a drug used to treat dry eye disease. Check out structure! Mechanism unknown.
💉Epcoritamab (Epkinly), a bispecific CD20-directed CD3 T-cell engager used to treat relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) in adults.
💊 Sulbactam/durlobactam (Xacduro), a co-packaged medication used for the treatment of bacterial pneumonia caused by Acinetobacter baumannii-calcoaceticus complex. It contains sulbactam, a beta-lactam antibacterial and beta-lactamase inhibitor; and durlobactam, a beta-lactamase inhibitor.
💊 Nirmatrelvir/ritonavir (Paxlovid), a co-packaged medication used as a treatment for COVID‑19. It contains the antiviral medications nirmatrelvir and ritonavir. Nirmatrelvir is a SARS-CoV-2 main protease inhibitor while ritonavir is a HIV-1 protease inhibitor and strong CYP3A4 inhibitor.
💉Flotufolastat F-18 (Posluma), a radiopharmaceutical diagnostic agent used in PET imaging to visualize PSMA-positive lesions in men with prostate cancer with suspected metastasis or recurrence.
💊 Sotagliflozin (Inpefa), a dual SGLT1/2 inhibitor used to reduce the risk of CV, hospitalization for heart failure, and urgent heart failure visit in adults with heart failure or type 2 diabetes mellitus, chronic kidney disease, and other cardiovascular risk factors
💉Glofitamab (Columvi), a bispecific mAb directed against CD20 and CD3 which is used for the treatment of relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.
💊 Ritlecitinib (Litfulo), a dual JAK3/TEC kinase family inhibitor used to treat severe alopecia areata in adults and adolescents 12 years and older.
💉Rozanolixizumab (Rystiggo), a humanized mAb targeting the human neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn) used to treat generalized myasthenia gravis.
💉Somatrogon (Ngenla), a long-acting recombinant human growth hormone used as the long-term treatment of pediatric patients who have growth failure due to growth hormone deficiency.
Again, a fascinating collection from Chris de Savi!
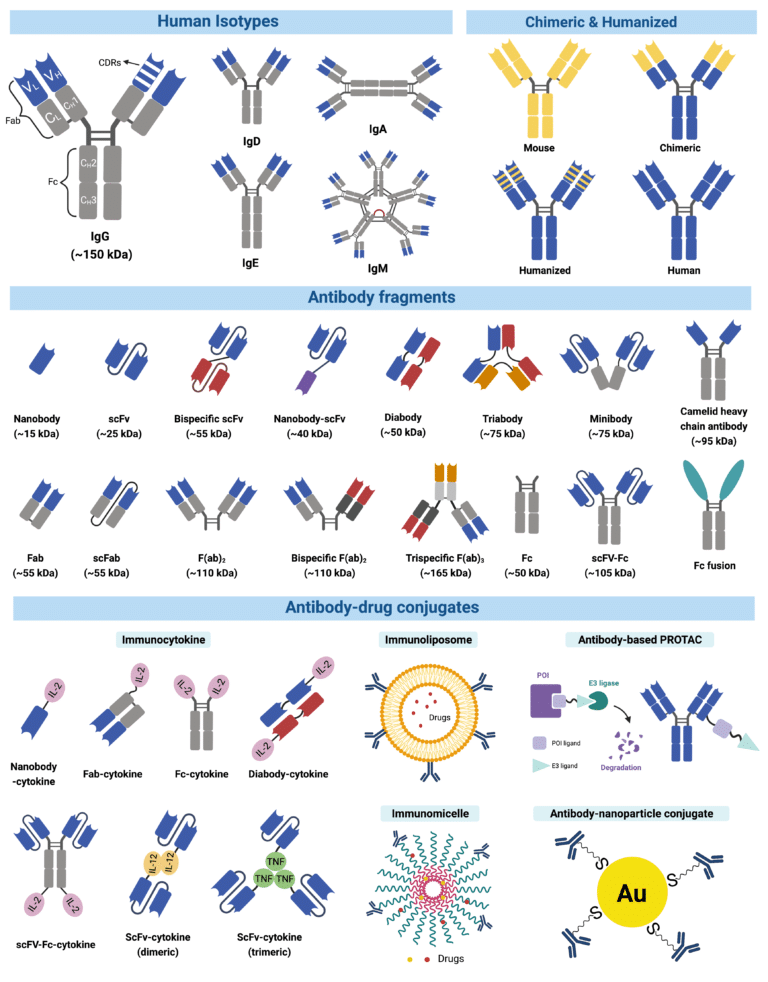
Interested in learning about monoclonal antibodies (mABs), how they are made, and what they are used for in research, diagnosis, and therapy?
Here is a nice article by Yuning Wang: What are Monoclonal Antibodies? – Rapid Novor
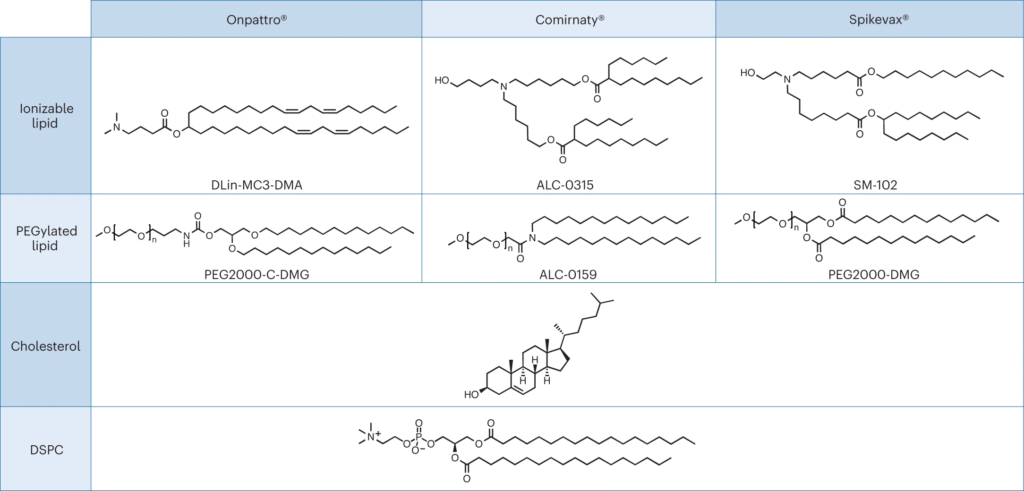
This is a fascinating question:
Are LNPs of mRNA drugs mere excipients or part of the drug?
Nanomedicines are complex drugs where components that have typically been regarded as excipients may now be considered part of the active ingredient. The distinction between the active ingredient and excipients for nanomedicines has important consequences for regulatory review and product development. The dissimilarity in the review of the recent RNA-based lipid nanoparticles highlights the need for further regulatory alignment on this topic.
To aid with this journey, both the US FDA and the European Medicines Agency have produced helpful guidelines. These documents, some specifically related to nanomedicines, provide the drug developer with a framework for selecting the appropriate regulatory path towards clinical trials and eventual product approval. The relevant pathway will then determine the type and amount of data that will be required for regulatory review. For example, a novel drug will likely require full Phase I to Phase III clinical trials, whereas a nano-formulation of an existing drug may qualify for an abridged/abbreviated review or as a generic formulation.
Dr. Eva Hemmrich & Scott McNeil
The fantastic story of a novel cyclodextrin API.
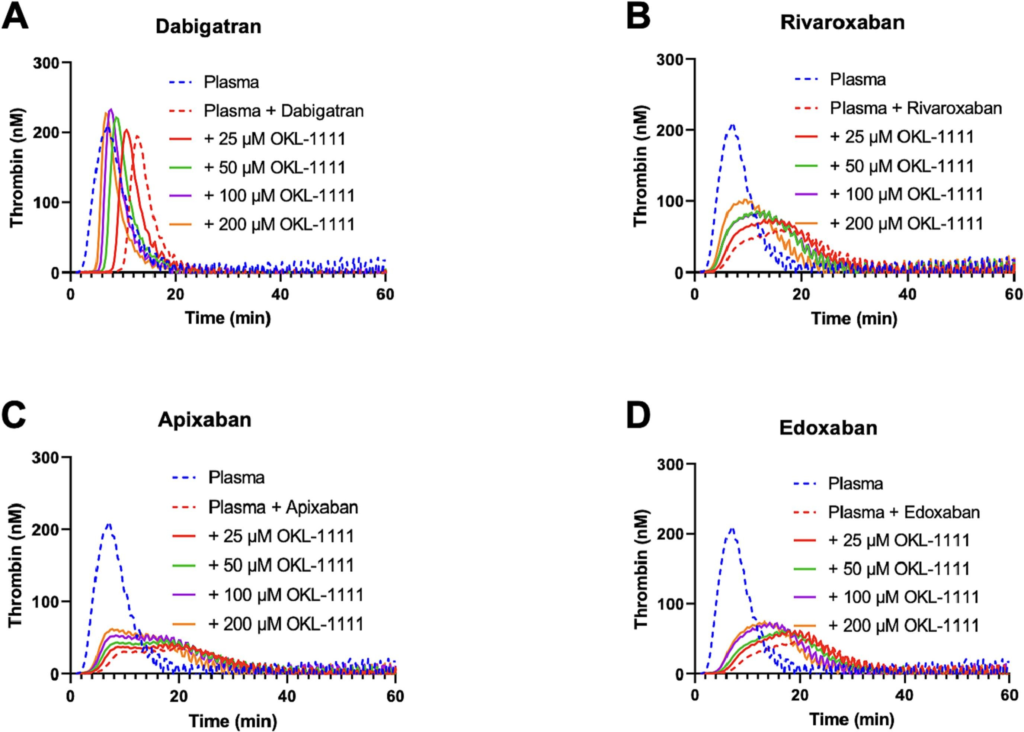
Antithrombotic therapy is inevitably associated with a risk of bleeding and these bleeding complications can be life-threatening. Recently, specific reversal agents were developed for the direct factor Xa and thrombin inhibitors (DOACs). However, next to the fact that these agents are relatively expensive, the use of selective reversal agents complicates the treatment of bleeding patients in practice. A class of cyclodextrins with procoagulant properties was recently discovered. the lead compound being OKL-1111.
OKL-1111 concentration-dependently reversed the in vitro anticoagulant effects of dabigatran, rivaroxaban, apixaban, and edoxaban in the thrombin generation assay. Also, in the absence of a DOAC, OKL-1111 concentration-dependently accelerated coagulation in this assay but did not initiate coagulation. The reversal effect was also seen for all DOACs in the rat tail cut bleeding model. In addition, when tested with other anticoagulants, OKL-1111 also reversed the anticoagulant effect of the vitamin K antagonist warfarin, the low molecular weight heparin enoxaparin, the pentasaccharide fondaparinux and the platelet inhibitor clopidogrel in vivo. OKL-1111 did not have prothrombotic effects in the Wessler model.
Alveron Pharma – Okklo Life Sciences – Sanquin
Joost Meijers, Kamran Bakhtiari, Alex Zwiers, Stephan Peters