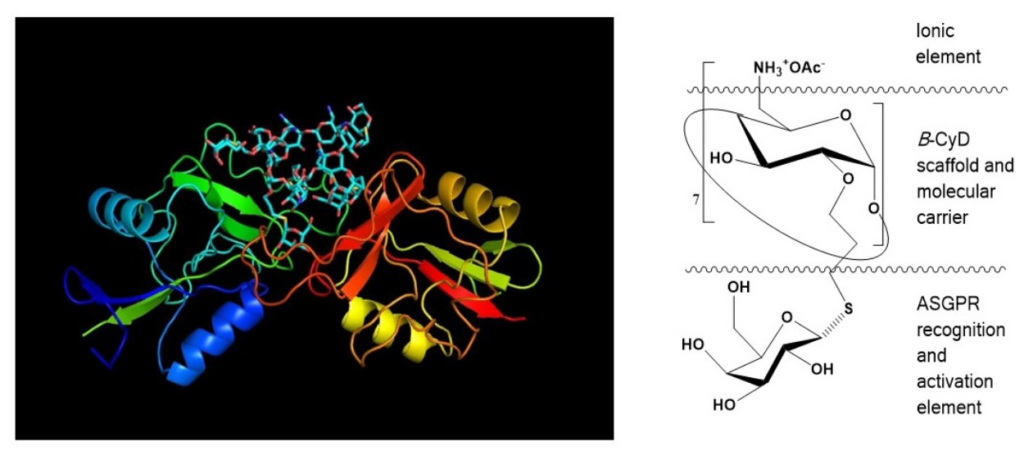
Today’s cyclodextrin is an innovative formulation of isosorbide mononitrate. In this patent, a cyclodextrin complex is prepared, suitable to develop sprays, having the advantages of quick response, small irritation, and convenience in use.
Isosorbide mononitrate is a medication primarily used for the prevention of angina pectoris, which is chest pain caused by reduced blood flow to the heart. It works by relaxing and widening blood vessels, which allows more blood and oxygen to reach the heart, thereby reducing the heart’s workload and helping to prevent episodes of chest pain. It belongs to a class of drugs known as nitrates.
Isosorbide mononitrate is used in a long-acting form, which is not suitable for relieving an acute angina attack but is used regularly to decrease the frequency and severity of angina episodes. It may also be used in other conditions as determined by a doctor, based on its vascular effects.
It is typically available in tablet form for oral administration. This medication is taken by mouth and is formulated as either immediate-release or extended-release tablets, depending on the intended dosing schedule and therapeutic need. The drug acts by releasing nitric oxide, which helps to relax and widen blood vessels, but the drug itself is solid in its delivery form.
Espacenet – Isosorbide mononitrate spray and preparation method thereof