Hydroxypropyl-β-Cyclodextrin Depletes Membrane Cholesterol and Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Entry into HEK293T-ACEhi Cells
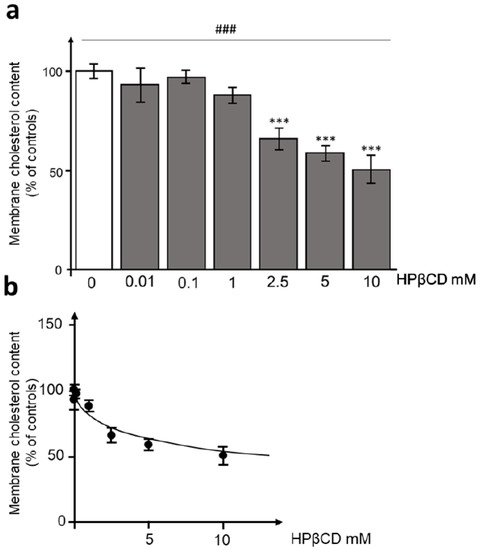
Vaccination has drastically decreased mortality due to coronavirus disease 19 (covid19), but not the rate of acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection. Alternative strategies, such as inhibition of virus entry by interference with angiotensin-I-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptors could be warranted. Cyclodextrins (CDs) are cyclic oligosaccharides that are able to deplete cholesterol from membrane lipid rafts, causing ACE2 receptors to relocate to areas devoid of lipid rafts. To explore the possibility of reducing SARS-CoV-2 entry, hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin (HPβCD) was tested in a HEK293T-ACE2hi cell line stably overexpressing human ACE2 and Spike-pseudotyped SARS-CoV-2 lentiviral particles. Exposure of HEK293T-ACEhi cells to concentrations of HPβCD starting from 2.5 mM to 10 mM showed a concentration-dependent reduction of approximately 50% of the membrane cholesterol content. In addition, incubation of HEK293T-ACEhi cells with HIV-S-CoV-2 pseudotyped particles in the presence of increasing concentrations of HPβCD (from 0.1 to 10 mM) displayed a concentration-dependent effect on SARS-CoV-2 entry efficiency. These data indicate that HPβCD is a candidate for use as a SARS-CoV-2 prophylactic agent.
Silvia Alboni, Valentina Secco, Bianca Papotti, Antonietta Vilella, Maria Pia Adorni, Francesca Zimetti, Laurent Schaeffer, tascedda fabio, Michele Zoli, Pascal Leblanc, Erica Villa
See the full article here: Hydroxypropyl-β-Cyclodextrin Depletes Membrane Cholesterol and Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Entry into HEK293T-ACEhi Cells