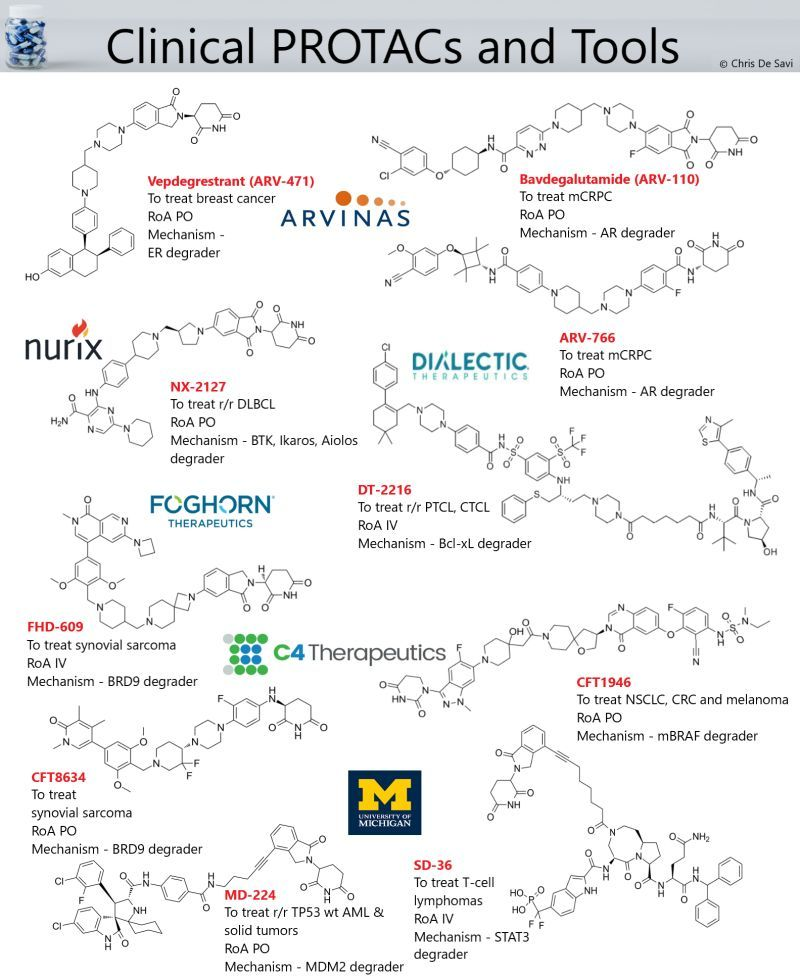
Clinical Degrader Drugs
Targeted protein degradation (TPD) is an emerging field in drug discovery that aims to selectively remove disease-causing proteins from cells. By directly targeting and eliminating proteins, TPD has the potential to address a wider range of disease targets, including those that have been traditionally considered “undruggable.”
Many highly selective PROTAC molecules with improved drug-like properties are entering clinical trials.
Some of the most exciting compounds being profiled are highlighted below
💊Vepdegrestrant (ARV-471), an orally bioavailable estrogen receptor (ER) protein degrader for the treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic ER+/HER2- breast cancer.
💊Bavdegalutamide (ARV-110), an orally bioavailable androgen receptor (AR) protein degrader for the treatment of metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC).
💊ARV-766, an orally bioavailable AR degrader for the treatment of mCRPC.
💊NX-2127, an orally bioavailable Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK), Ikaros (IKZF1) and Aiolos (IKZF3) degrader for the treatment of R/R B cell malignancies.
💊NX-5948, an orally bioavailable BTK degrader for the treatment of R/R B cell malignancies.
💉DT-2216, an IV administered selective B-cell lymphoma-extra large (Bcl-XL) protein degrader for the treatment of T-cell lymphomas.
💉FHD-609, an IV administered BRD9 protein degrader for the treatment of synovial sarcoma.
💊CFT1946, an orally bioavailable mutant BRAF kinase protein degrader for the treatment of various BRAF V600E-driven cancers.
💊CFT8634, an orally bioavailable BRD9 protein degrader for the treatment of synovial sarcoma.
💊KT-474, an orally bioavailable IRAK4 protein degrader for the treatment hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) and atopic dermatitis (AD).
💉KT-413, an IV administered IRAK4, IKZF1 and IKZF3 protein degrader for the treatment of MYD88-mutant B cell lymphomas.
💉KT-333, an IV administered STAT3 protein degrader for the treatment of Peripheral T-cell Lymphoma (PTCL).
💉KT-253, an IV administered MDM2 protein degrader for the treatment of r/r high grade myeloid malignancies and solid tumors.
Tools
💉SD-36, an IV administered STAT3 tool protein degrader.
💉MD-224, an IV administered MDM2 tool protein degrader.
Another amazing summary from Chris De Savi.