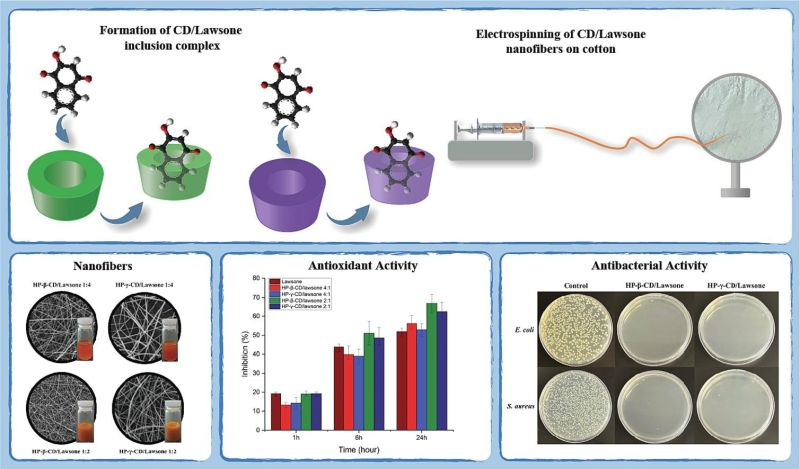
Functionalization of cotton nonwoven with cyclodextrin/lawsone inclusion complex nanofibrous coating for antibacterial wound dressing
Today’s cyclodextrin is a new type of wound dressing developed at Cornell University by Tamer Uyar‘s team.
Bioactive compounds like lawsone offer dual benefits of wound healing and infection prevention, however, their limited solubility and viability hinder their applications. To address this, Hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin (HP-β-CD) and Hydroxypropyl-gamma-cyclodextrin (HP-γ-CD) were employed.
Electrospinning yielded smooth and uniform nanofibers with an average diameter of ∼300–700 nm. The nanofibers exhibited ∼100 % loading efficiency of lawsone and its rapid release upon dissolution.
Notably, antibacterial assays demonstrated the complete elimination of Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus colonies. The CD/lawsone nanofibers also showed suitable antioxidant activity ranging from 50% to 70%.